-
[System Security] 3.4 Virtual Memory 관리Security/System Security 2021. 4. 4. 19:18
Virtual Memory
- 사용자 입장에서 보이는 논리적인 메모리
- 필요한 블럭들만 Physical Momory에 적재시킴으로써 메모리를 절약



가상 메모리의 공간을 분할하는 기법
- Segmentation 기법
- Paging 기법
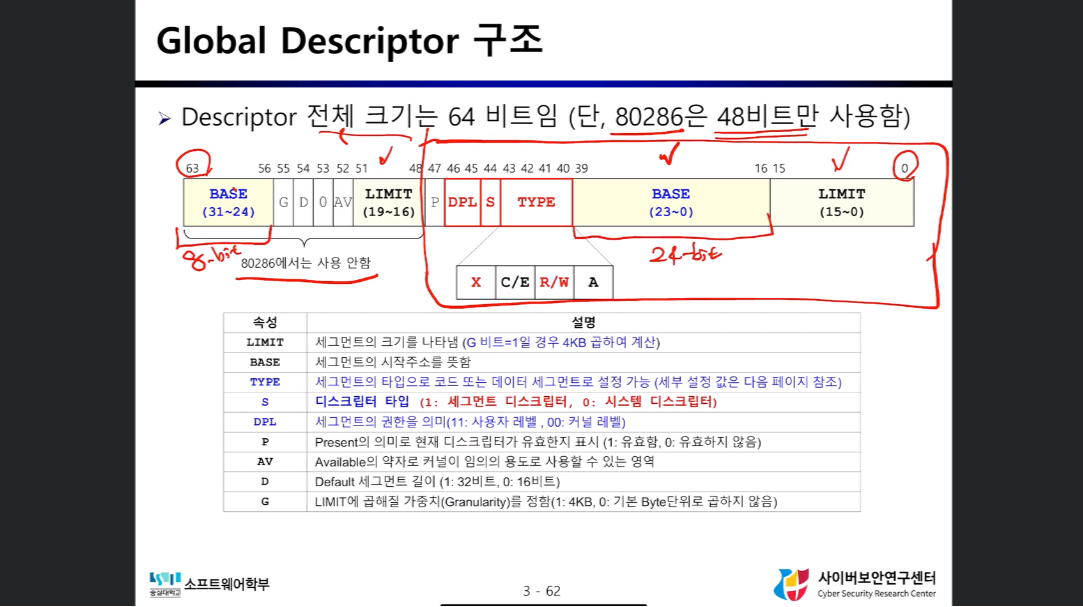
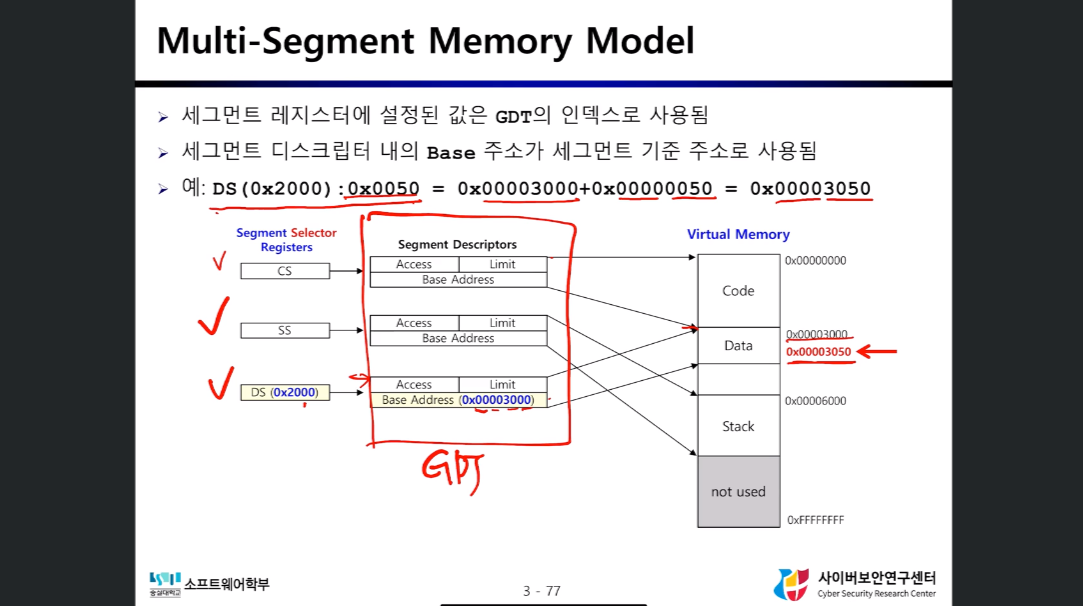
Segmentation Address Resolution
- GDT로 Virtual Address의 Segment 비트(16비트)를 Physical Address의 Segment 위치(Base, Limit)로 변환한다
- Virtual Address의 offset 비트(32비트)를 찾아낸 Segment의 위치와 더해 실제 주소를 구한다

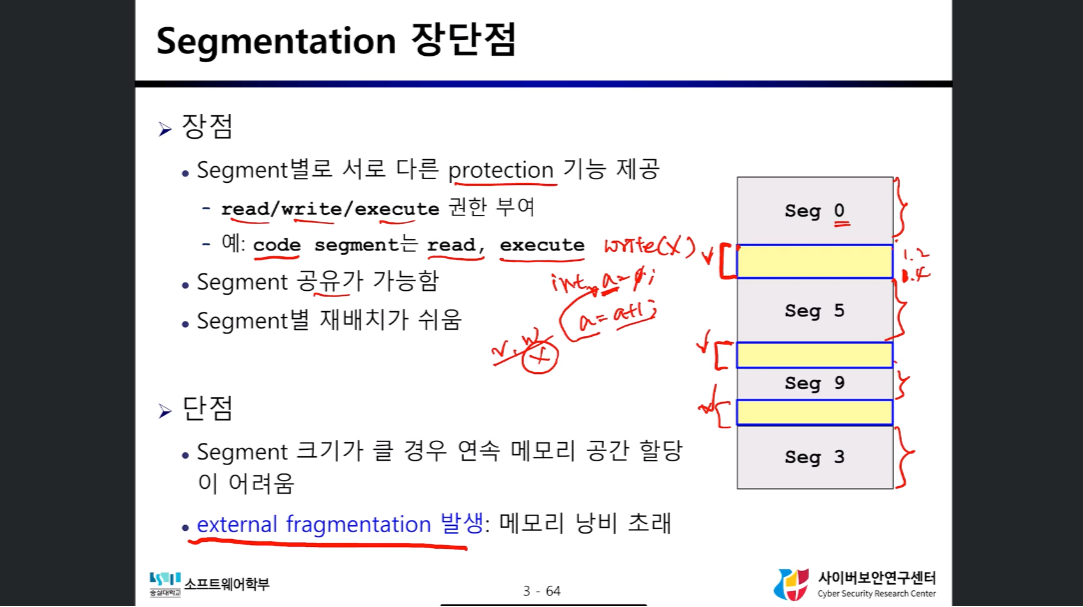
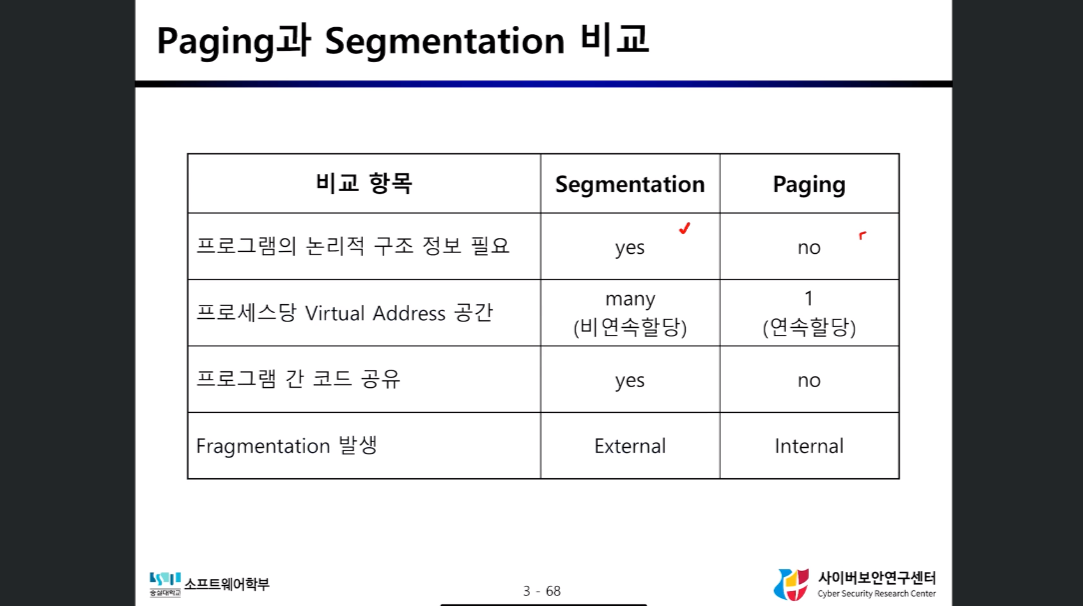
Segmentation 장점
- Segment별로 서로 다른 protection 기능 제공 (Code Segment의 경우 write 권한 X)
- Segment 공유 가능
- Segment별 재배치가 쉬움
Segmentation 단점
- external fragmentation 발생
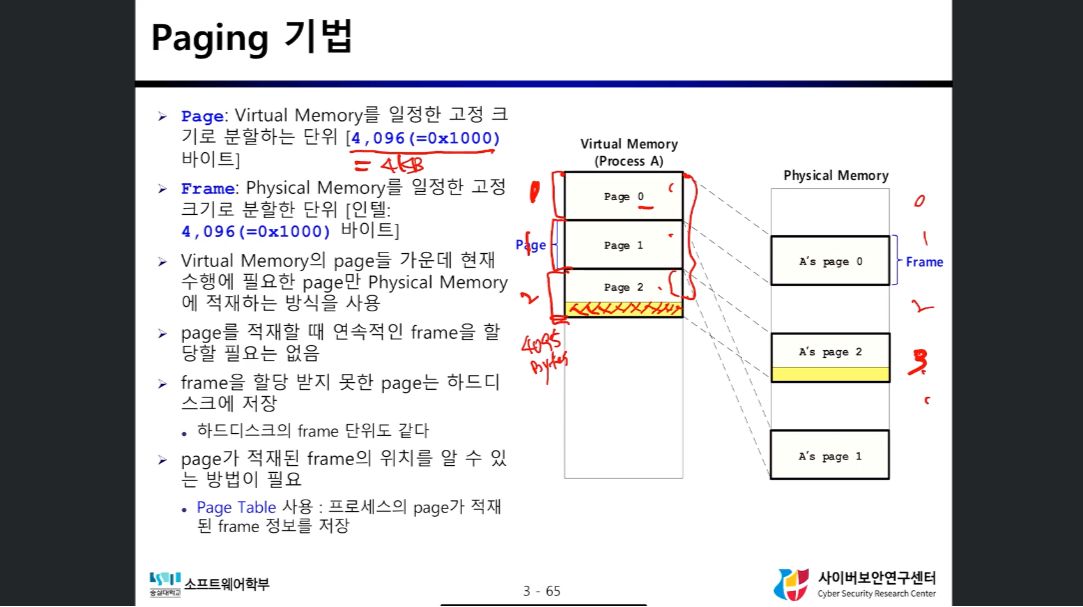
Paging
- Virtual Memory를 일정한 고정 크기(Page)로 분할하여 Physical Memory에 할당하는 방식
- 할당된 Page는 Frame이라고 한다
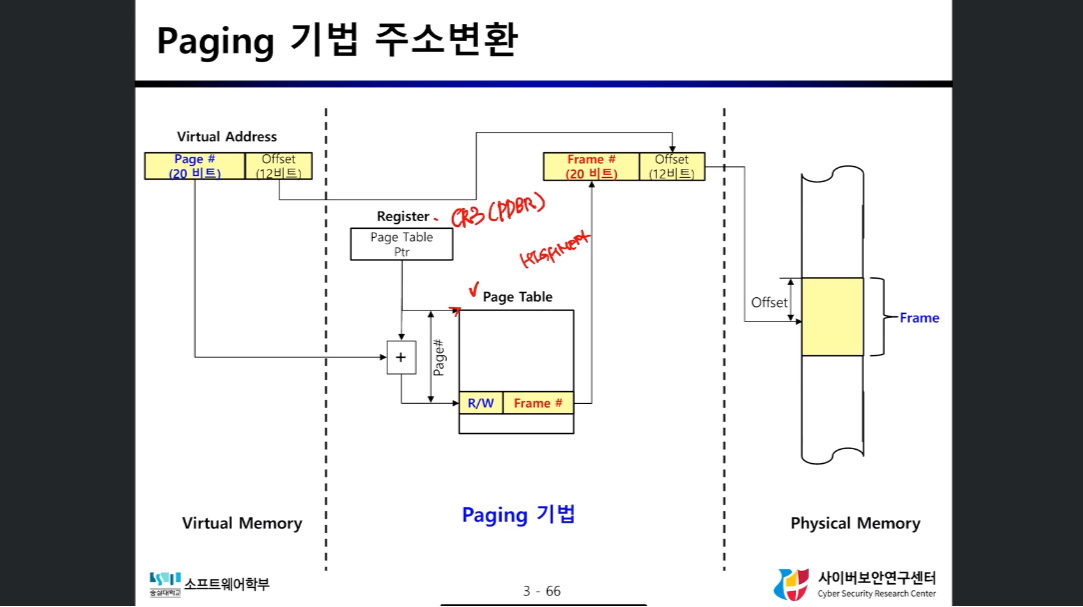
Paging Address Resolution
- Virtual Address의 Page 20비트가 페이지 테이블을 참조하여 Frame의 시작 주소가 된다
- 페이지 테이블의 주소는 PDBR(Page Directory Base Register)을 참고한다
Paging 기법의 장점
- 메모리 할당과 해제가 빠르다
- 할당 : free page list에서 첫 page를 할당
- 해제 : 해당 page를 free page list에 추가
Paging 기법의 단점
- Internal Fragmentation 발생
- 프로세스마다 마지막 page에서 fragmentation 발생
- page 크기각 클 수록 낭비되는 메모리 공간이 많아짐
- 프로그램 공유, 보호가 어렵다

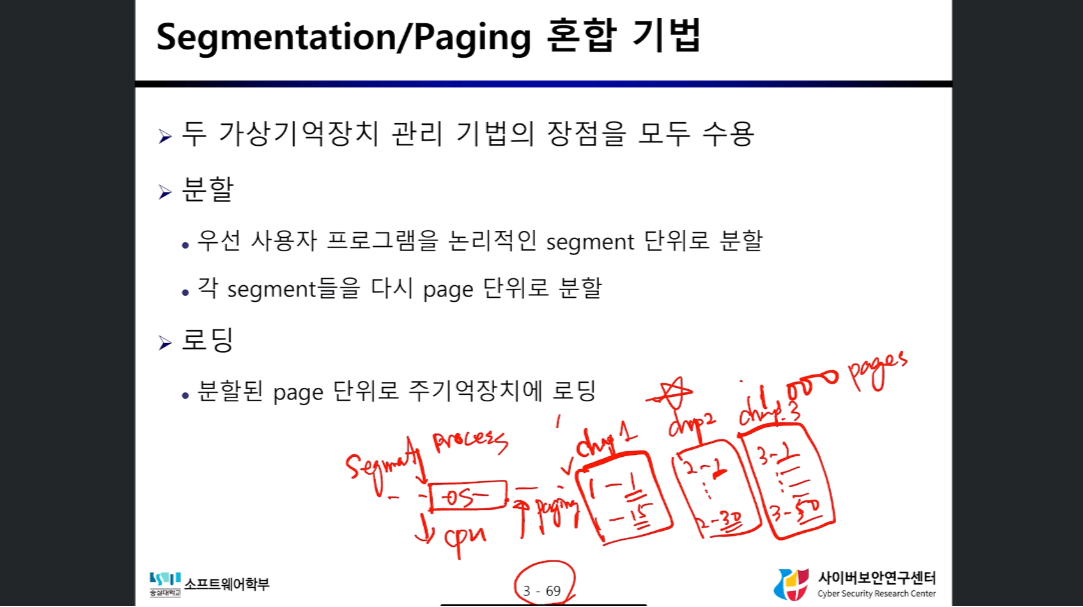
혼합 기법
- 프로그램을 논리적인 segment 단위로 나누고 그 이후 page 단위로 한번 더 나눈다
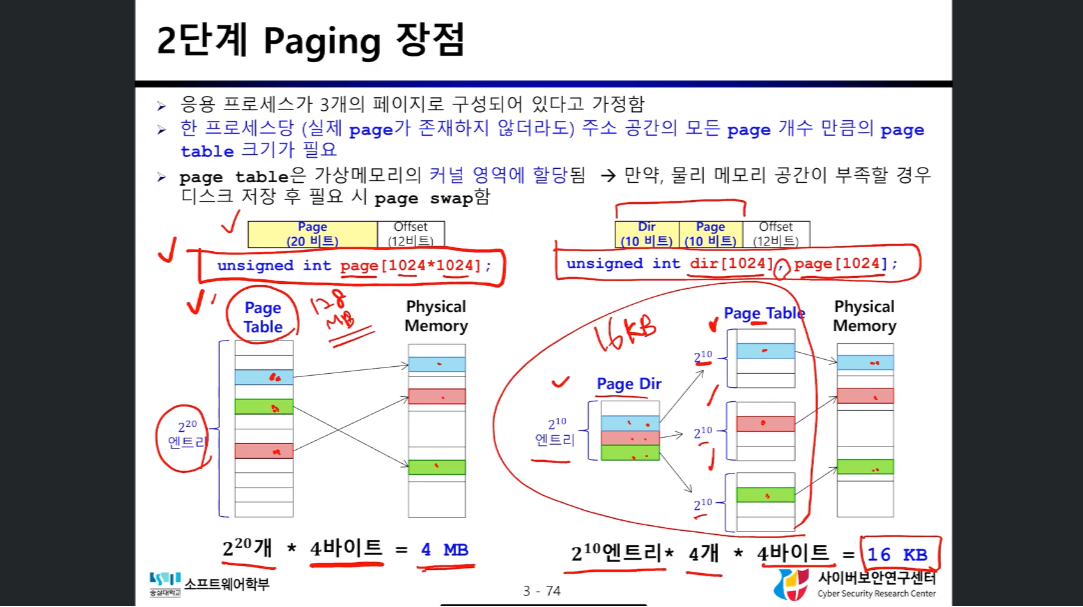
2단계 Paging 장점
- Page Directory는 사용하는 페이지의 정보를 담고 있으므로 사용하지 않는 페이지만큼의 메모리를 절약할 수 있다
windows의 경우 2단계, 리눅스의 경우 3,4단계 Paging 사용
Multi-Segment Memory Model
- SS(Stack Segment), CS(Code Segment), DS(Data Segment) 등 각 Segment의 Base 주소를 레지스터에 저장한다
Flat-Segment Memory Model
- Intel에서 정의한 Multi-Segment Memory Model 을 사용하지 않고 Base, Limit 주소를 0, MAX로 사용한다
'Security > System Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
[System Security] 4.1 리눅스 프로세스 주소공간 (0) 2021.04.05 [System Security] 3.5 80x86 동작 모드와 부팅 (0) 2021.04.04 [System Security] 3.3 Register 구조 (0) 2021.04.04 [System Security] 3.2 80x86 프로세서 구조 (0) 2021.04.04 [System Security] 3.1 운영체제 개요 (0) 2021.04.04